Symphony SNMP support is built upon Microsoft's Extendible SNMP Agent. During Symphony installation, the Symphony SNMP Extension-Agent is registered with Microsoft's SNMP Agent by modifying the Windows registry.
Symphony traps for unauthorized logins and all alarms when they occur or when the user marks them.
Ensure that Microsoft's SNMP Windows Component is installed and set to start automatically with Windows.
Task 1: Enable SNMP in Symphony
1. Log into the server. Click Settings>General Settings.
2. In the SNMP group area, select the Enabled check box and click Save.
3. Restart Symphony services: Starting and Stopping Services.
Task 2: Configure SNMP Service Security
Microsoft’s SNMP Agent supports SNMP v2c; therefore, the SNMP Agent must be configured with the accepted community names and hosts.
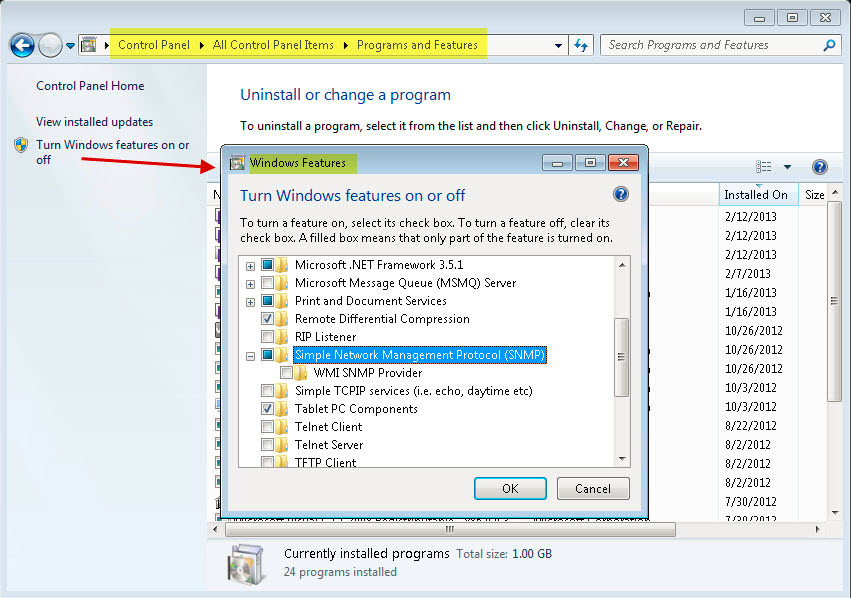
1. Ensure that SNMP service is installed on your machine: Control Panel>Programs and Features>Windows Features>Simple Network Management Protocol(SNMP) check box.

2. Ensure that you are logged on as local administrator; otherwise, depending on your Windows operating system, the Security tab in the SNMP Service Properties dialog box will not be accessible or visible.
3. Via the Windows Services management console, open the properties of the SNMP Service.
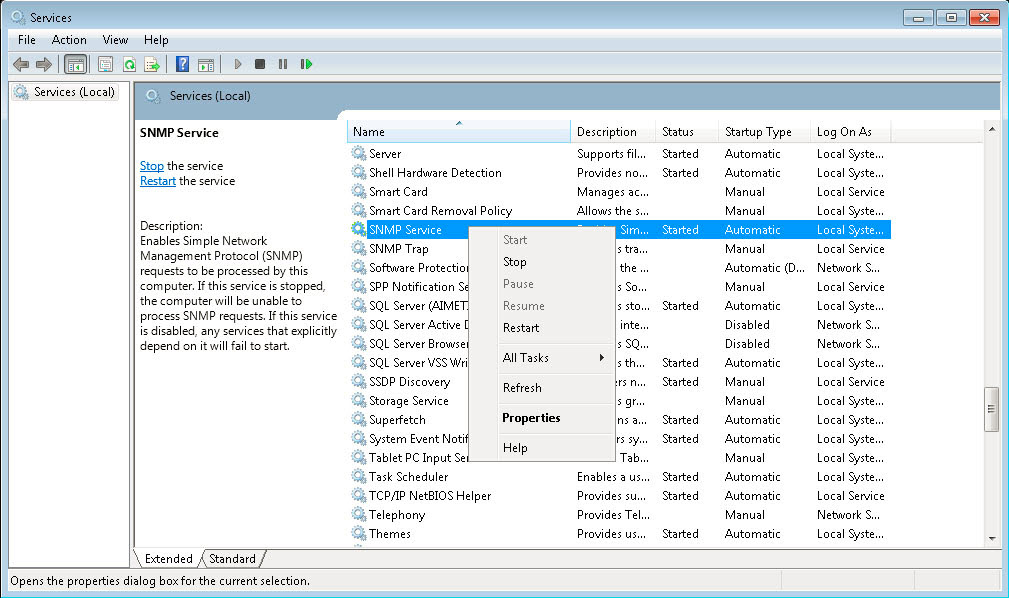
4. Click the Security tab.
.jpg)
5. Create the desired communities (for example “public=” community with “READ ONLY” rights)
6. (Optional) Restrict which hosts may issue SNMP requests.
7. Click OK.
1. Start the Symphony services:
From the Server menu, select Services, and then Start Symphony Services.
At this time, SNMP data is provided by the AI InfoService and AI Watchdog
services.
The AI Watchdog service is responsible for providing the service status SNMP values, and AI InfoService all other values.
The AI SNMP Registry serves as a registration of all the sub-agents (and is used by our SNMP Extension Agent).
The Symphony management values are rooted at object-identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.34101.1.
2. Use an SNMP software package to query the SNMP Agent. For example, you can use a GUI tool such as the iReasoning MIB Browser: http://ireasoning.com/mibbrowser.shtml.
3. Start the MIB Browser and open the Server mib files. The mib files are typically located in the program files: C:\Program Files\Aimetis\Symphony\mib files.
4. If you are using the iReasoning MIB Browser, for example, you must load the Server mib files into the browser: File>Load MIBs. In the file manager that opens, navigate to and select the mib files (Vendor.mib, Server.mib).
5. Additionally, for SNMP using UDP, set SNMP Retries to 2. (Tools>Options>General tab, SNMP Retries=2 field.)
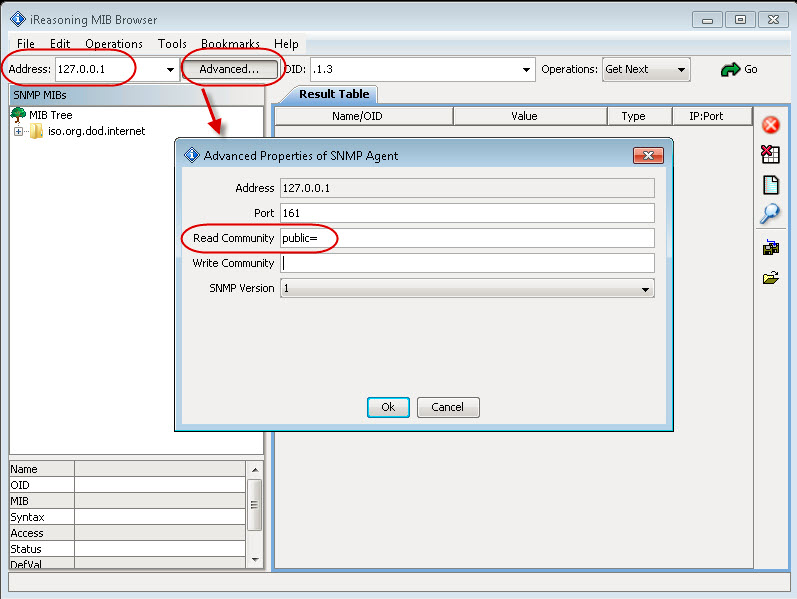
6. Enter 127.0.0.1 as the address and edit advanced options to point the program to your read community (for example “public=” community with “READ ONLY” rights).
7. Walk all the management values currently available within the Symphony sub-tree.
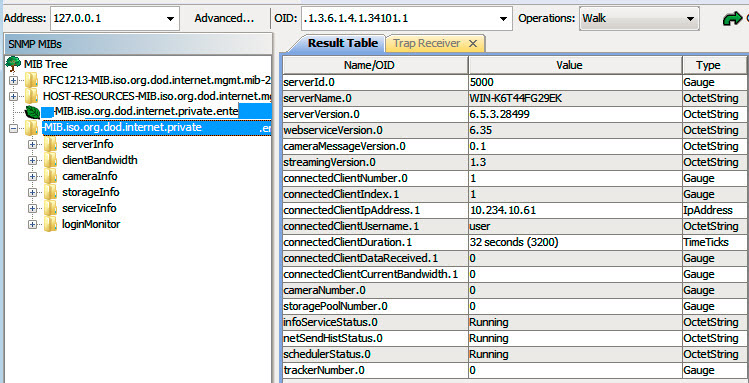
Object-identifier descriptions
Category |
Details |
Description |
Trap Yes/No |
serverInfo |
serverId |
|
|
|
serverName |
Server Computer Name |
|
versionInfo |
serverVersion |
Assembly version of the Symphony server |
|
|
webserviceVersion |
Version for Symphony web-service protocol |
|
|
cameraMessageVersion |
Version for Symphony camera message protocol |
|
|
streamingVersion |
Version for Symphony streaming protocol |
|
clientBandwidth |
connectedClientNumber |
Number of connected clients to this Symphony server |
|
|
connectedClientIndex |
Unique value for each connected client |
|
|
connectedClientIpAddress |
IP address the client is connected from |
|
|
connectedClientUsername |
Username that the client is connected with |
|
|
connectedClientDuration |
Duration that the client has been connect to this server |
|
|
connectedClientDataReceived |
Data received, in Kbytes, by the client via this connection |
|
|
connectedClientCurrentBandwidth |
Current bandwidth, in Kbytes per second, between client and this server |
|
cameraInfo |
cameraNumber |
Number of cameras managed by this server |
|
|
cameraId |
Unique identifier for the camera |
|
|
cameraName |
Name of camera |
|
|
footagePath |
Path to camera’s footage |
|
|
footageSize |
Size of camera’s footage in bytes |
|
storageInfo |
storagePoolNumber |
Number of storage pools managed by this server |
|
|
storagePath |
Path to the storage pool |
|
|
storageCapacity |
Capacity of storage pools in Mbytes |
|
|
storagePercentAvailable |
Available capacity in the storage pool, as a percentage of storageCapacity |
|
|
storageFootageSize |
Size of footage within the storage pool in Mbytes |
|
|
storageFootageFiles |
Number of footage files in the storage pool. |
|
serviceInfo |
infoServiceStatus |
Status of AI InfoService service |
|
|
netSendHistStatus |
Status of AI NetSendHist service |
|
|
schedulerStatus |
Status of AI Scheduler service |
|
|
trackerNumber |
Number of tracker services |
|
|
trackerId |
The ID of the tracker |
|
|
trackerStatus |
Status of the AI Tracker service for the trackerID |
|
loginMonitor |
authorizedLoginNotif |
Notification sent when a login is successful |
Yes |
|
unauthorizedLoginNotif |
Notification sent when an unauthorized login is attempted |
Yes |
|
loginNotifyIpAddress |
IP address that the client is connected from |
|
|
loginNotifyUsername |
Username that the client is attempting to login with |
|
|
loginNotificationMessage |
Message with additional details about the login attempt |
|
alarmMonitor |
alarmNotif |
Notification sent when an alarm occurs or is marked |
Yes |
|
alarmNotifyCameraId |
Camera ID of the camera that recorded the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyCameraName |
Camera name of the camera that recorded the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyUserId |
User ID of the user that marked the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyUserName |
User name of the user that marked the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyMarkedDelay |
Time alarm was marked |
|
|
alarmNotifyFalseAlarm |
Is this a false alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyRuleId |
Rule ID of the rule causing the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyRuleName |
Rule name of the rule causing the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyDBId |
ID of the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyComment |
Comments associated with the alarm |
|
|
alarmNotifyMSSinceChange |
Number of milliseconds between when the alarm occurred and when it was detected |
|
deviceMovementMonitor |
devicesMovedNotif |
Notification sent when a device is moved from one server to another (manual device move or failover swap) |
Yes |
|
sourceServerId |
ID of the server that devices moved from |
|
|
destinationServerId |
ID of the server that devices moved to |
|
|
numberDevicesMoved |
Number of devices moved from source to destination server |
|
healthMonitor |
healthMonitorFaultNotification |
Notification sent when the health monitor detects a fault |
Yes |
|
healthMonitorActionNotification |
Notification sent when the health monitor takes an action in response to a fault |
Yes |
|
healthMonitorName |
Name of the associated health monitor |
|
|
healthMonitorAction |
Name of the action taken |
|
Additional Tools and Information
If you prefer a command line tool instead of a GUI MIB Browser, you can use a free command line tool (Net-SNMP) to walk the mib files. (The snmpwalk command will perform a sequence of chained GETNEXT requests automatically.)
• For instructions, see Net-SNMP: http://net-snmp.sourceforge.net/
The following sites also provide information on SNMP:
• How SNMP Works: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc783142.aspx
• How to effectively use a MIB Browser: http://www.unleashnetworks.com/resources/articles/88-how-to-effectively-use-a-mib-browser.html